When your computer refuses to boot, it can be a frustrating and perplexing experience. Understanding the common issues and their solutions can help you troubleshoot and potentially fix the problem without needing professional assistance. This article delves into the various reasons why a computer might not boot and offers practical solutions to get your system up and running again.
Common Hardware Issues
Power Supply Problems
One of the most frequent causes of a computer not booting is a faulty power supply. If your computer shows no signs of life—no lights, no fans, no sounds—then the power supply might be the culprit. To diagnose this, check if the power cable is securely connected to both the computer and the wall outlet. You can also try using a different power cable or outlet to rule out external issues.
If the power supply is indeed the problem, replacing it is usually straightforward. Ensure you purchase a power supply that matches your computer’s specifications. If you’re not comfortable doing this yourself, seeking professional help is advisable.
Loose or Faulty Components
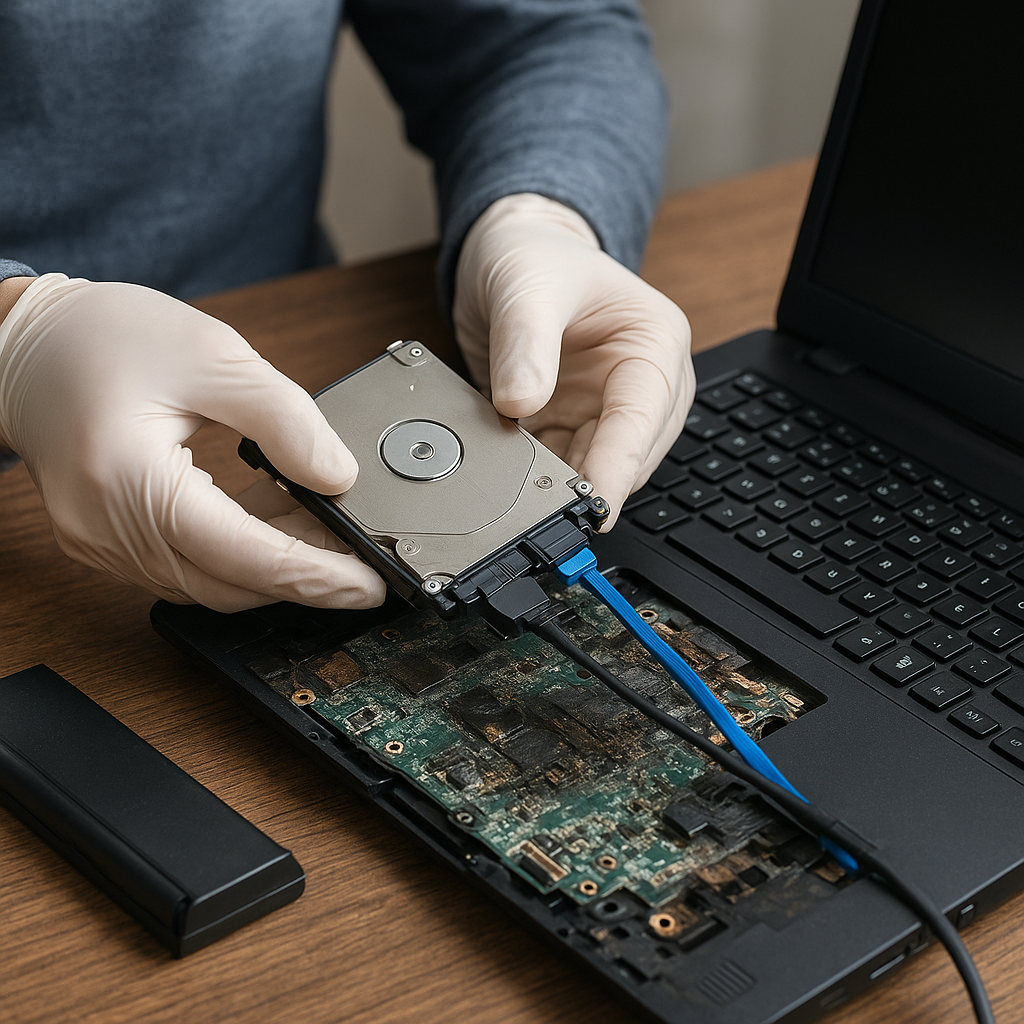
Another common hardware issue involves loose or faulty components inside the computer. Over time, components like RAM, graphics cards, and hard drives can become dislodged. Open your computer case and ensure all components are securely seated in their respective slots. Pay special attention to the RAM and graphics card, as these are often the culprits.
If reseating the components doesn’t work, you might have a faulty piece of hardware. Testing each component individually in another working computer can help identify the faulty part. Replacing the defective component should resolve the boot issue.
Software and Firmware Issues
Corrupted Operating System
A corrupted operating system can prevent your computer from booting. This can happen due to a failed update, malware infection, or file corruption. If you suspect this is the issue, you can try booting into Safe Mode. Safe Mode loads a minimal set of drivers and can sometimes bypass the corruption, allowing you to troubleshoot further.
If Safe Mode works, you can attempt to repair the operating system using built-in tools like System Restore or Startup Repair. If these tools fail, you might need to reinstall the operating system. Ensure you back up your data before proceeding with a reinstallation.
BIOS/UEFI Settings
Incorrect BIOS or UEFI settings can also prevent your computer from booting. The BIOS/UEFI is responsible for initializing hardware components and loading the operating system. If these settings are misconfigured, your computer might fail to boot.
To access the BIOS/UEFI, restart your computer and press the designated key (usually F2, F10, or Delete) during startup. Once inside, you can reset the settings to their default values. This often resolves boot issues caused by incorrect configurations. If you recently updated your BIOS/UEFI, consider rolling back to a previous version if the update introduced the problem.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
Bootable Recovery Media
If basic troubleshooting steps fail, creating bootable recovery media can be a lifesaver. This involves using a USB drive or DVD with a bootable version of your operating system or a specialized recovery tool. Booting from this media allows you to access your system and perform repairs without relying on the potentially corrupted internal drive.
To create bootable recovery media, you’ll need access to another working computer. Download the necessary files from the official website of your operating system or recovery tool, and follow the instructions to create the bootable media. Once created, insert the media into your non-booting computer and restart it. You may need to change the boot order in the BIOS/UEFI to prioritize the USB drive or DVD.
Professional Diagnostic Tools
For more complex issues, professional diagnostic tools can provide deeper insights into why your computer won’t boot. These tools can test various hardware components, analyze system logs, and identify software conflicts. While some of these tools are available to consumers, others are typically used by IT professionals.
If you’ve exhausted all other options, consulting a professional who has access to these diagnostic tools might be the best course of action. They can perform a thorough analysis and recommend the most effective solution to get your computer back in working order.
Preventive Measures
Regular Maintenance
Preventing boot issues is often easier than fixing them. Regular maintenance can help keep your computer in good working condition. This includes keeping your operating system and drivers up to date, running antivirus scans, and cleaning the interior of your computer to prevent dust buildup.
Additionally, regularly backing up your data ensures that you won’t lose important files if your computer does encounter a serious issue. Using cloud storage or an external hard drive can provide peace of mind and make recovery easier if something goes wrong.
Monitoring Hardware Health
Monitoring the health of your hardware components can also prevent boot issues. Tools like SMART (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) can provide early warnings of hard drive failures. Similarly, monitoring the temperatures of your CPU and GPU can help you identify cooling issues before they cause damage.
Many modern motherboards come with built-in health monitoring features accessible through the BIOS/UEFI. Regularly checking these can help you catch potential problems early and take corrective action before they lead to boot failures.
In conclusion, a computer that won’t boot can be a daunting problem, but understanding the common issues and their solutions can make troubleshooting more manageable. Whether the issue is hardware-related, software-related, or a combination of both, the steps outlined in this article can help you diagnose and fix the problem. Regular maintenance and monitoring can also prevent many boot issues, ensuring your computer remains reliable and functional.